Mobius Poem by Endwar


Here is a link to a wonderful Mobius Poem by Endwar. Very Nice!
Click here for the Mobius Poem


Here is a link to a wonderful Mobius Poem by Endwar. Very Nice!
Click here for the Mobius Poem
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
10:32 PM
1 comments
![]()

Do the muses scatter ancient fragments of thought or do they just perpetuate them. How is it that the ancient Greek Titans can still speak?
also see Orthogonal Space Poem
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
11:50 PM
0
comments
![]()
Labels: orthogonal space poem, prometheus, Pushcart Prize in Poetry
The Virtuous Sphere (part two)
This blog entry is a continuation of “The Virtuous Sphere” please read the last blog entry so that today’s will make sense.
On the last blog entry, we had just finished talking about the equation of a sphere. However, the next question one may ask is, “why are there words in the equations instead of numbers?” To answer this question, you should read my essay on verbogeometry. I am going to republish some of the essay that relates to “The Virtuous Sphere” but if you have not read the essay on verbogeometry then you may not get as much out of this as you would if you were to read it.
Distance Formula and Verbogeometry: As we have seen, to calculate the distance between two points, we need to describe our points by its coordinates using the nomenclature of the coordinate pair. Let me reiterate, describing a point in verbogeometry is no different from numerical coordinates except we use words. Lets look again at the example in figure 15 where we used the midpoint formula to find the exact point between the points: P1(love,praise) and P2(hate,punishment) but instead of putting them in the midpoint formula lets put them in the distance formula. (See below)
 Here we have an expression for the distance between the points P1(love,praise) and P2(hate,punishment) in two dimensions. But we can also use verbogeometry in any number of dimensions including hyper-dimensions. But before we look at hyper dimensional verbogeometry lets look at another example which we will express in the third dimension. The following example uses a three dimensional Cartesian coordinates system with 3 simple antonym word-axes. (See below) The first axis is noble / ignoble the second axis is just / unjust and the third axis is loyal / disloyal.
Here we have an expression for the distance between the points P1(love,praise) and P2(hate,punishment) in two dimensions. But we can also use verbogeometry in any number of dimensions including hyper-dimensions. But before we look at hyper dimensional verbogeometry lets look at another example which we will express in the third dimension. The following example uses a three dimensional Cartesian coordinates system with 3 simple antonym word-axes. (See below) The first axis is noble / ignoble the second axis is just / unjust and the third axis is loyal / disloyal. Now lets look at the expression for the distance between the points P1(noble,just,loyal) and P2(ignoble,unjust,disloyal) (see below)
Now lets look at the expression for the distance between the points P1(noble,just,loyal) and P2(ignoble,unjust,disloyal) (see below) Notice the green line in figure 33 is the visual representation for the mathematical expression above. However, it would be much easier to visualize if we were able to rotate the axis. Figure 33 is an isometric view, which I chose to use because it is best for viewing the axis but unfortunately at the expense of viewing the spatial orientation of the green line.
Notice the green line in figure 33 is the visual representation for the mathematical expression above. However, it would be much easier to visualize if we were able to rotate the axis. Figure 33 is an isometric view, which I chose to use because it is best for viewing the axis but unfortunately at the expense of viewing the spatial orientation of the green line.
(The virtuous sphere is written in the language of three dimensions. What I find interesting is that we can write a spherical equation in hyper dimensions. The following shows the distance formula written in a hyperdimension.)
Now let us look at verbogeometry in a hyper-dimension. Let us look at the distance formula used in seven dimensions:Figure 35 shows the mathematical poem 1+1+1+1+1+1+1+1 =1 This is a metaphorical piece that creates a metaphoric path from the concept of confusion, to where seven deities meet. The piece uses the analytic geometry distance formula in a seven dimensional space where each dimension is a gradation from confusion to a point where a deity exists.
Here is a detail:
 Lets look at the coordinate pairs for these two points P1(confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion) and P2(Allah,Buddha,Jesus,Spider woman,Vishnu,Yahweh,Zeus)
Lets look at the coordinate pairs for these two points P1(confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion, confusion) and P2(Allah,Buddha,Jesus,Spider woman,Vishnu,Yahweh,Zeus)
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
3:49 PM
0
comments
![]()
The Virtuous Sphere (part one)

I thought it would be a nice idea to post "The Virtuous Sphere" and talk some about it. First of all I would like to say that I believe there are many ways to define virtue, this is only an artist rendition of one way. Please do not get bound up here in the idea of some absolute truth… remember the Hindu saying: “All wars are Just on both sides” When this piece was originally mediated to me my intentions were not so much interested in an answer of denotation but in the aesthetic inherit with the structure of a mathematical sphere and the coloration and distortion of that sphere by the personal ideas of integrity, justice, nobility and of course virtue.
Today's blog entry will talk about the analytic geometry involved in the piece and the next blog entry will discuss the verbogeometrical ideas needed to approach this piece.
Let me talk a little about the mechanics of this piece. This piece is a standard verbogeometry piece so obviously I will be borrowing sections from my essay on verbogeometry to help open this up for you that are not familiar.
We all should be able to recognize a sphere, but did you know that a sphere has a relationship to the Pythagorean Theorem? To see this relationship we first should talk about the relationship between the distance formula and the Pythagorean Theorem. Then we will look at the relationship between the distance formula and a circle and after that the sphere. The distance formula uses the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate distances on the Cartesian coordinate system. The Pythagorean Theorem says that the square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the square of it sides. Solve for c and we get the following:
Solve for c and we get the following:
Let us look at little closer at how the Pythagorean Theorem works in a Cartesian coordinate system. Here is an example: Plot two points on a two-dimensional axis system P1(-9,10) and P2(4,3) and If we draw a lines between the points and lines parallel to the axes we can obtain a right triangle.
 To solve the length of the hypotenuse we first find the difference between the x values and the y values to create the sides of the triangle then we plug the values into the Pythagorean Theorem. The x value is 9 - 4 = 5 and the y value is 10 - 3 = 7Now we plug it to the equation and we get the expression in the following figure:
To solve the length of the hypotenuse we first find the difference between the x values and the y values to create the sides of the triangle then we plug the values into the Pythagorean Theorem. The x value is 9 - 4 = 5 and the y value is 10 - 3 = 7Now we plug it to the equation and we get the expression in the following figure:
 The distance or length of the hypotenuse would be the square root of 74 or approximately 8.602
The distance or length of the hypotenuse would be the square root of 74 or approximately 8.602
The distance formula in two dimensions is thus -- Given two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2):
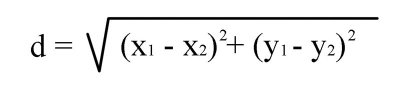 To reiterate -- you will notice that the distance formula is nothing more than Pythagorean Theorem placed on a Cartesian coordinate system! The x1-x2 in our equation actually shifts the line horizontally and the y1-y2 shifts the line vertically. In effect if we start at the origin for our point (x1,y1) then we can simplify the equation as shown below:
To reiterate -- you will notice that the distance formula is nothing more than Pythagorean Theorem placed on a Cartesian coordinate system! The x1-x2 in our equation actually shifts the line horizontally and the y1-y2 shifts the line vertically. In effect if we start at the origin for our point (x1,y1) then we can simplify the equation as shown below:
 Let us look at the equation for a circle: (below) --- Doesn’t it also look remarkably like the Pythagorean Theorem? In essence it is the Pythagorean Theorem! Notice that the radius of the circle corresponds to the hypotenuse of the right triangle. What we do is sort of ‘nail down’ one end of our right triangle at the hypotenuse and spin it around so that the other end of the hypotenuse follows the form of a circle.
Let us look at the equation for a circle: (below) --- Doesn’t it also look remarkably like the Pythagorean Theorem? In essence it is the Pythagorean Theorem! Notice that the radius of the circle corresponds to the hypotenuse of the right triangle. What we do is sort of ‘nail down’ one end of our right triangle at the hypotenuse and spin it around so that the other end of the hypotenuse follows the form of a circle. All of the equations that we have been looking so far function in two dimensions but what if we wanted to use the Pythagorean Theorem in three dimensions? To use the Pythagorean Theorem or the distance formula in three dimensions we append another term at the end of the equation so it looks like the one below.
All of the equations that we have been looking so far function in two dimensions but what if we wanted to use the Pythagorean Theorem in three dimensions? To use the Pythagorean Theorem or the distance formula in three dimensions we append another term at the end of the equation so it looks like the one below.
 The Pythagorean Theorem in three dimensions is the same as it was in two dimensions except that we add another term at the end to give us the extra dimension.
The Pythagorean Theorem in three dimensions is the same as it was in two dimensions except that we add another term at the end to give us the extra dimension.
Let us look at the equation for a sphere (below):
 Notice that it looks just like the Pythagorean Theorem in three dimensions? It follows the same thought that we did in two dimensions. Where we ‘nail down’ one end of the triangle and spin it around in a circle but since we are in three dimensions, we also spin the circle around an axis and so it goes that the end of the triangle we started with now follows the form of a sphere.
Notice that it looks just like the Pythagorean Theorem in three dimensions? It follows the same thought that we did in two dimensions. Where we ‘nail down’ one end of the triangle and spin it around in a circle but since we are in three dimensions, we also spin the circle around an axis and so it goes that the end of the triangle we started with now follows the form of a sphere.
This concludes discussing the analytic geometrical aspects of “The Virtuous Sphere” You can see that I used the equation for a sphere as my mathematical language for this piece. The only thing we haven’t discussed is the verbogeometric properties of the piece. The next entry in my blog will discuss some of the mechanics of verbogeometry that are needed to approach this piece.
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
1:25 PM
0
comments
![]()
I studied with Robert C. Morgan in the late 1970’s and he is responsible for much of my earlier artistic development. He exposed me to the conceptual art movement in general and Benar Venet in particular. Venet noticed that science had aesthetics as well as art and was bold enough to re-contextualize these scientific aesthetics as Art. It wasn’t until I read the Dancing Wu Li Masters by Gary Zukav that I experienced an epiphany that drove me into mathematics and science. Prior to that event I had no interest in mathematics and some disdain. However, I must say I loved math up until I was seven years old then, as I mentioned, I abandoned it until 1979.
Robert has always been supportive and I always wish the best for him.
Millennium Film Workshop
presents
A Screening of Super-8 films by Robert C. Morgan
Saturday, June 17, 2006, at 8 PM
Although known today primarily as a critic and curator, Robert Morgan
emerged as a "post-conceptual" artist in the mid-seventies. Between 1974 -1989,
Morgan worked in a variety of different media, including an extensive body
of work in Super-8 film. He regards his films as "counter-narrative" in that
they deconstruct both Hollywood and commercial television -- the two primary
forms of visual narrative in the entertainment industry -- by laminating appropriated
footage against a personal and often political narrative. This is a rare opportunity
to see films by one of the formative "appropriation" artists of the seventies.
A reception will precede the screening in the Millennium Gallery at 7 PM
Admission: $8 / $6 (members)
For further information, please contact:
Millennium Film Workshop
66 East 4th Street, NYC 10003
Tel & Fax: (212) 673 - 0090
Email: cinema@millenniumfilm.org
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
11:00 PM
0
comments
![]()

The image above has been simmering in the background for a few years now and has finally come to fruition. It came about in December 2001 over a cup of coffee while taking a break at the ASCI conference in NYC. At the conference I met a very interesting Poet/Artist Philosopher and NASA scientist named Farzad Mahootian. We had a wonderful conversation between sips of dark java in mid town Manhattan and talked of many things. I shared my ideas on verbogeometry while he shared his ideas on sculptures that purify the environment. In our mutual excitement he thought it would be a good idea to incorporate the two ideas into a piece of Art. The piece above is the result. I decided to make a symbolic wedge from a verbogeometric prism and have it cleaning the air with chrysanthemum power.
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
8:40 PM
2
comments
![]()
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
8:04 PM
2
comments
![]()
Labels: equational poetry, mathematical visual poetry, mathematics poetry, number poetry, Visual Mathematical Poetry
Posted by
Kaz Maslanka
at
7:20 PM
0
comments
![]()